Table of Contents
The crypto industry evolves rapidly, and one term that’s been getting a lot of attention lately is BlockDAG.
Whether it’s being discussed in relation to trending presale tokens, bold promises of ultra-fast speeds, or even being measured up to Bitcoin, BlockDAG is generating buzz. But what exactly does it mean? Is it a breakthrough tech advancement, a popular DAG-based crypto project, or perhaps both?
If you’re unsure what to make of it, you’re not alone. The hype is undeniable, but real explanations are sometimes hard to come by. This post is here to clear things up. We’ll walk through what BlockDAG really is, how it differs from blockchain, and highlight the trending BDAG project that’s been fueling much of the curiosity.
By the end, you’ll have a solid grasp on:
- What BlockDAG means in tech terms
- How it operates and how it stands apart from traditional blockchain
- The BlockDAG (BDAG) project and its current presale
- The benefits and potential downsides of BlockDAG systems
- Where BlockDAG stands in comparison to other crypto DAGs
- How BlockDAG might be applied in the real world
Let’s break it down.
BlockDAG: What It Is and Why It Matters
BlockDAG stands for Block Directed Acyclic Graph. Like blockchain, it’s a type of distributed ledger—but instead of relying on a single chain of blocks, it uses a graph-based structure. This change in architecture opens the door to faster transactions and improved scalability. There’s also a specific cryptocurrency called BlockDAG that utilizes this approach.
Understanding BlockDAG: The Technology Behind the Buzz
Before diving into individual projects or evaluating their investment potential, it’s important to get familiar with the underlying tech. BlockDAG represents a shift in how decentralized systems manage data—taking the core concept of Bitcoin’s ledger and reimagining its structure.
What Is a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG)? A Simple Breakdown
Let’s simplify things with a metaphor. Think of a to-do list where certain tasks can’t begin until others are done. Task A needs to be completed prior to starting tasks B and C, while task D is dependent on the completion of task B before it can begin. You use arrows to show these dependencies. There are no cycles—nothing loops back.
That’s essentially what a DAG is:
- Directed: Data flows in a single direction, similar to how tasks depend on previous ones.
- Acyclic: There are no loops or backtracking.
- Graph: A graph is a structure of nodes (points) linked together by connections called edges.
In the world of crypto, nodes may signify single transactions or complete blocks, depending on the network’s structure.
How BlockDAG Is Different from Traditional Blockchains Like Bitcoin
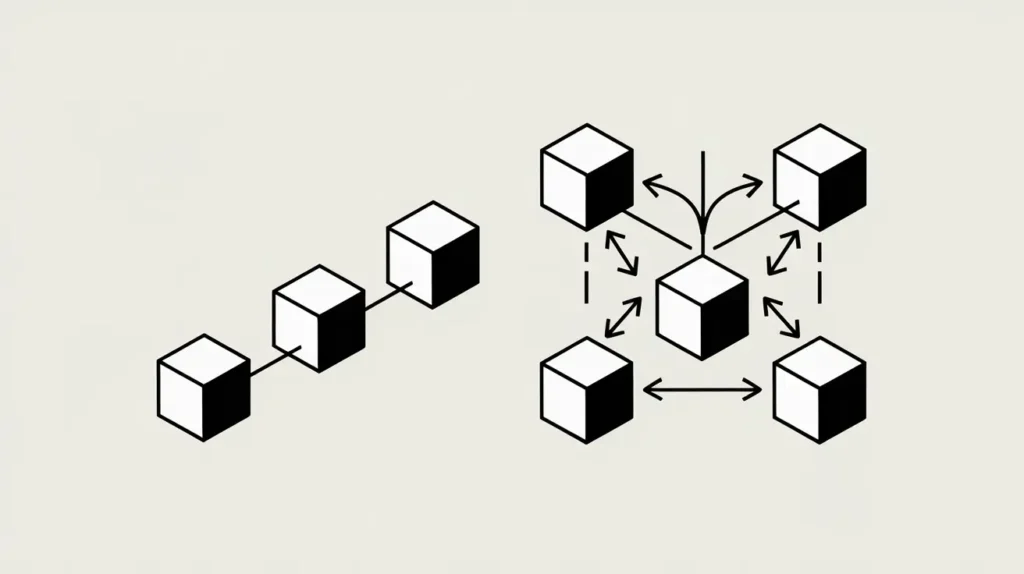
The major difference lies in how data is organized. Bitcoin’s blockchain uses a straight-line structure where each block connects only to the previous one. This leads to delays since the network allows only a single block to be appended worldwide at a time. When multiple blocks are mined simultaneously, some get discarded.
BlockDAG offers a network-like structure where blocks can be added more flexibly.
| Feature | Blockchain (e.g., Bitcoin) | BlockDAG |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Linear chain | Network-style graph |
| Block Addition | One at a time | Multiple blocks in parallel |
| Speed | Slower confirmations | Faster potential confirmations |
| Scalability | Limited | Potentially higher TPS |
| Orphan Blocks | Frequent | Minimized or reused |
In essence: Blockchain = slow, one-lane road. BlockDAG = fast, multi-lane highway.
The Mechanics: How BlockDAG Processes Transactions
So how does this graph-based approach actually work in practice?
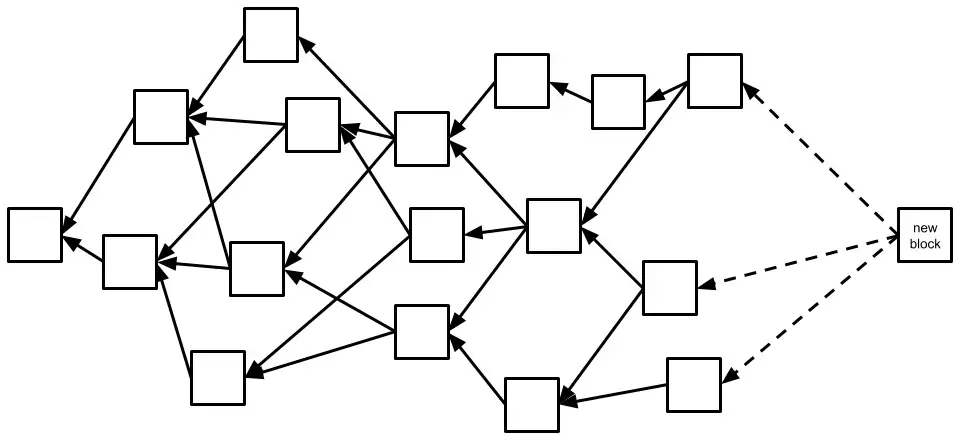
- Multiple Block Links: Instead of each block pointing to just one previous block, it can reference several. This results in a complex web-like structure instead of a straightforward linear chain.
- Transaction Finality: Finalizing transactions involves certain rules. While not always instant, the deeper a transaction sits in the structure, the more secure and permanent it becomes. Certain BlockDAG protocols, such as GHOSTDAG and PHANTOM, are designed to establish a well-defined transaction sequence.
- Consensus Algorithms: BlockDAGs can implement modified versions of Proof-of-Work or Proof-of-Stake as consensus mechanisms to verify blocks and transactions, customized to suit the graph structure. This process guarantees synchronization of the network’s state and its transaction history.
This approach aims to solve blockchain’s famous “trilemma”—balancing decentralization, security, and scalability—by improving scalability without heavily compromising the other two.
The BlockDAG (BDAG) Cryptocurrency Project
Note: The following is a look at the BDAG project based on public sources such as the whitepaper and official website (as of 2025).
A big reason people are googling “what is BlockDAG” is due to a specific project that has adopted the same name. Let’s explore the BlockDAG (BDAG) crypto and its current presale phase.
Project Overview: What Is BlockDAG (BDAG) All About?
As stated in its official documentation, the BlockDAG project is developing a decentralized and scalable ecosystem powered by its own version of BlockDAG technology. Its key objectives include:
- Achieving much faster transactions than standard blockchains
- Facilitating tiny, rapid microtransactions
- Supporting decentralized applications (dApps)
- Providing accessible mining solutions via mobile devices
- Merging blockchain-grade security with DAG-speed performance
Key Features Claimed by the BlockDAG Project
The project highlights several features based on its BlockDAG architecture:
- Consensus: They often mention a hybrid consensus mechanism combining elements of PoW and DAG-based ordering protocols.
- Speed & Scalability: Claims often include transaction confirmation times measured in seconds and a potential throughput reaching thousands of TPS.
- Compatibility: Information regarding EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) compatibility is crucial for dApp development – check their official documentation for current status.
- Mining: Often promotes accessibility through traditional mining rigs and mobile mining applications (evaluate the mechanism and rewards carefully).
Remember to treat claimed figures, especially projected TPS, with caution until proven on a live mainnet under real-world load.
BlockDAG Coin (BDAG) Tokenomics (If Publicly Available)
Understanding the tokenomics of the BDAG crypto is essential:
- Total Supply: Check official sources for the maximum supply of BlockDAG coin (BDAG).
- Distribution: How is the supply allocated? Look for details on:
- BlockDAG Presale: Percentage allocated to early buyers across different presale coin batches. This is often a significant portion for new projects seeking funding. Many investors look for the best crypto presale opportunities, but risks are high.
- Team Allocation: How much is reserved for the founding team (vesting schedules are important).
- Ecosystem/Development Fund: Funds set aside for future growth, partnerships, marketing.
- Mining/Staking Rewards: Allocation for network participants securing the network post-launch.
- Coin Utility: What will BDAG be used for? Common utilities include transaction fees, staking, governance votes, accessing platform services, or rewards within the ecosystem.
Source: Tokenomics details are typically outlined in the project’s whitepaper or on the official BlockDAG website.
Project Roadmap & Current Status (e.g., Presale Info)
Timeliness is critical here.
- Roadmap: Review their published roadmap for key milestones: Testnet launch, Mainnet launch, exchange listings, feature rollouts (e.g., dApp platform, smart contracts).
- Current Status: As of 2025, the BlockDAG project is actively running its crypto presale, structured in batches with the coin price increasing at each stage. Always verify the current batch and pricing directly from the source. Visit the Official BlockDAG Project Website (DYOR)
Monitor the roadmap progress compared to initial promises — delays are common in crypto projects. For the latest developments, check out our in-depth BlockDAG News & Stories for 2025.
The Team Behind BlockDAG (If Public & Verifiable)
Is the team public or anonymous?
- Public Team: Look for names, LinkedIn profiles, and track records of the core team members on their official website. A public, experienced team can add credibility.
- Anonymous Team: If the team is anonymous or uses pseudonyms, it presents an additional layer of risk that potential users or investors must consider.
Advantages of BlockDAG Technology (and the Project’s Claims)
Why is there excitement around BlockDAG technology? It promises several potential benefits over traditional blockchains:
- ✅ Increased Scalability & Throughput: By allowing parallel block processing, BlockDAGs can potentially handle significantly more transactions per second (TPS).
- ✅ Faster Transaction Confirmation Times: Transactions can often be confirmed much faster due to the graph structure and specialized consensus algorithms.
- ✅ Improved Energy Efficiency: While dependent on the specific consensus used, some BlockDAG implementations (especially those not solely reliant on intensive PoW) could be more energy-efficient than Bitcoin.
- ✅ Reduced Orphan Block Rate: The DAG structure inherently minimizes or incorporates blocks that would be orphaned in a linear chain, reducing wasted computational resources.
- ✅ Potential for Decentralization: While needing careful design, the ability for many nodes to participate in block creation simultaneously could enhance decentralization compared to systems where mining power concentrates.
The specific BlockDAG project leverages these technological premises in its claims and marketing.
Potential Challenges and Risks of BlockDAGs
Despite the potential, BlockDAG technology and specific projects like the BlockDAG crypto face challenges and risks:
- ❗ Security Models: BlockDAG security is different and less battle-tested than traditional blockchain security (like Bitcoin’s PoW). Potential attack vectors (like controlling a large percentage of network hashing power for malicious purposes) might manifest differently and require novel defense mechanisms.
- ❗ Centralization Risks: Some DAG implementations have relied on centralized “coordinator” nodes or limited validator sets initially to order transactions or prevent certain attacks, which compromises decentralization. It’s crucial to examine the specific project’s mechanisms.
- ❗ Complexity: Understanding, implementing, and securing BlockDAG protocols is generally more complex than traditional blockchains.
- ❗ Adoption & Network Effect: As a newer technology, BlockDAGs need to build trust, attract users, developers, and achieve a strong network effect to be truly successful and secure.
- ❗ Project-Specific Risks (Especially for Presales):
- Execution Risk: The team may fail to deliver on their roadmap or technology promises.
- Market Volatility: The price of BDAG crypto (and any presale coin) can be extremely volatile, especially upon listing on exchanges. View BDAG Price on CoinMarketCap.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The crypto space faces evolving regulations globally.
- Presale Risks: Investing in crypto presales is highly speculative. There’s no guarantee the project will launch successfully, get listed on major exchanges, or achieve its goals. Many presale projects fail.
Financial Disclaimer: Investing in cryptocurrencies, especially new projects and crypto presales like the BlockDAG presale, involves substantial financial risk. You could lose your entire investment. Always perform thorough research (DYOR) and consult a qualified financial advisor before making any investment decisions. For a detailed analysis, read our comprehensive review: Is BlockDAG Legit?
BlockDAG vs. Other DAG Cryptocurrencies (Kaspa, IOTA, Fantom, etc.)
BlockDAG isn’t the only crypto DAG technology or project. It’s helpful to see how it compares to others:
Comparison Table: DAG-Based Projects
| Feature | BlockDAG (Specific Project) | Kaspa (KAS) | IOTA (MIOTA) | Fantom (FTM) – Opera Chain |
| Core Structure | BlockDAG (Uses Blocks in DAG) | BlockDAG (Uses Blocks in DAG) | Blockless DAG (Tangle) | DAG for Consensus (Lachesis) |
| Consensus | Hybrid (PoW + DAG ordering – Verify) | PoW + GHOSTDAG Protocol | Coordinator (Pre-Coordicide) | Leaderless aBFT via DAG |
| Primary Focus | Scalability, Speed, dApps (Verify) | Fast PoW, Scalable Transactions | IoT, Fee-less Microtransactions | DeFi, dApps, EVM Compatibility |
(Note: This is a simplified comparison. Each project has deep technical nuances. Research thoroughly.)
- Kaspa: Employs a BlockDAG (GHOSTDAG) with Proof-of-Work, aiming for rapid block times and high throughput—positioning itself as a strong technological rival in the space.
- IOTA: Uses the “Tangle,” a unique blockless DAG where each new transaction verifies two previous ones, enabling scalability and feeless microtransactions. It’s designed for the Internet of Things (IoT), enabling fee-less microtransactions, although it still depends on a Coordinator node for security.
- Fantom: Uses a DAG structure (Lachesis) as part of its asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerant (aBFT) consensus mechanism to achieve fast finality for its blockchain (Opera), which is popular for DeFi and is EVM-compatible.
The specific BlockDAG project aims to carve its niche potentially through its unique blend of consensus, claimed performance metrics, and ecosystem features like mobile mining.
Potential Use Cases for BlockDAG Technology
If BlockDAG technology delivers on its promises of speed and scalability, it could unlock or enhance various applications:
- Internet of Things (IoT): Handling vast numbers of small transactions from connected devices efficiently.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Enabling faster settlement times for trades, loans, and other financial operations.
- Supply Chain Management: Tracking goods and information rapidly and transparently across complex supply chains.
- Decentralized Data Storage/Transfer: Facilitating quick and distributed movement of data.
- Micropayments & Streaming: Making tiny, frequent payments economically viable for content creators or services.
- Online Gaming: Supporting in-game economies and asset transfers with near-instant speed.
Conclusion: Is BlockDAG the Future?
So, what is BlockDAG? It’s undeniably an intriguing evolution in distributed ledger technology, offering a potential solution to the scalability limitations of traditional blockchains through its unique graph structure. The promises of faster speeds, higher throughput, and improved efficiency are compelling.
Simultaneously, the BlockDAG project currently in its crypto presale phase has captured significant attention by adopting this technology and name, aiming to build a comprehensive ecosystem around its BDAG crypto coin.
However, potential must be balanced with pragmatism. BlockDAG technology is newer and less battle-tested than blockchain. Security models are still evolving, and the risks associated with any new crypto venture, especially presale coin offerings, are substantial. Claims made during crypto presales require rigorous verification and a healthy dose of skepticism.
BlockDAG is an exciting innovation in the crypto space. Whether this project becomes the best crypto presale of 2025 or the technology sees wider adoption remains to be seen. For a closer look, read more on whether BlockDAG could be the next big thing in crypto. As always, thorough research and a clear understanding of the risks are essential before diving into this emerging sector.
BlockDAG FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
Is BlockDAG better than Bitcoin?
They represent different tradeoffs. BlockDAG technology aims for higher speed and scalability, potentially sacrificing some of the proven security, decentralization purity, and long track record of Bitcoin’s simpler, more robust linear chain and PoW consensus. “Better” depends on the specific use case.
Is BlockDAG a good investment?
Investing in any cryptocurrency, especially a presale coin like the BlockDAG coin (BDAG), is highly speculative and carries significant risk. Potential rewards might be high, but so is the chance of losing your investment. This article is not financial advice. Do Your Own Research (DYOR), understand the technology and tokenomics, evaluate the team, assess the risks, and never invest more than you can afford to lose.
How to buy BlockDAG coin (BDAG)?
the BDAG crypto coin is primarily available through the project’s official BlockDAG presale website. Be extremely cautious of unofficial links or platforms claiming to sell it. After the presale concludes, the project aims for listings on cryptocurrency exchanges, but there’s no guarantee of which exchanges or when. Always refer to the official project channels for legitimate purchasing information and be wary of scams.
What is the difference between BlockDAG and DAG?
DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) is the underlying mathematical structure. BlockDAG specifically refers to using this DAG structure to organize blocks containing transactions (like Kaspa or the BlockDAG project). Other crypto DAGs (like IOTA’s Tangle) might be “blockless,” where individual transactions form the nodes of the graph directly.
Who created BlockDAG?
For the specific BlockDAG project, check their official website or documentation for information on the founding team (whether public or anonymous). The concept of using DAG structures for distributed ledgers, including BlockDAG variations like GHOSTDAG, evolved from academic research and work by multiple computer scientists and cryptographers aiming to improve blockchain scalability.
Disclaimer: This blog post is for informational purposes only and should not be interpreted as financial advice. The author and publisher are not responsible for any investment decisions made based on this content. Always conduct comprehensive research on your own before getting involved with any cryptocurrency project.





